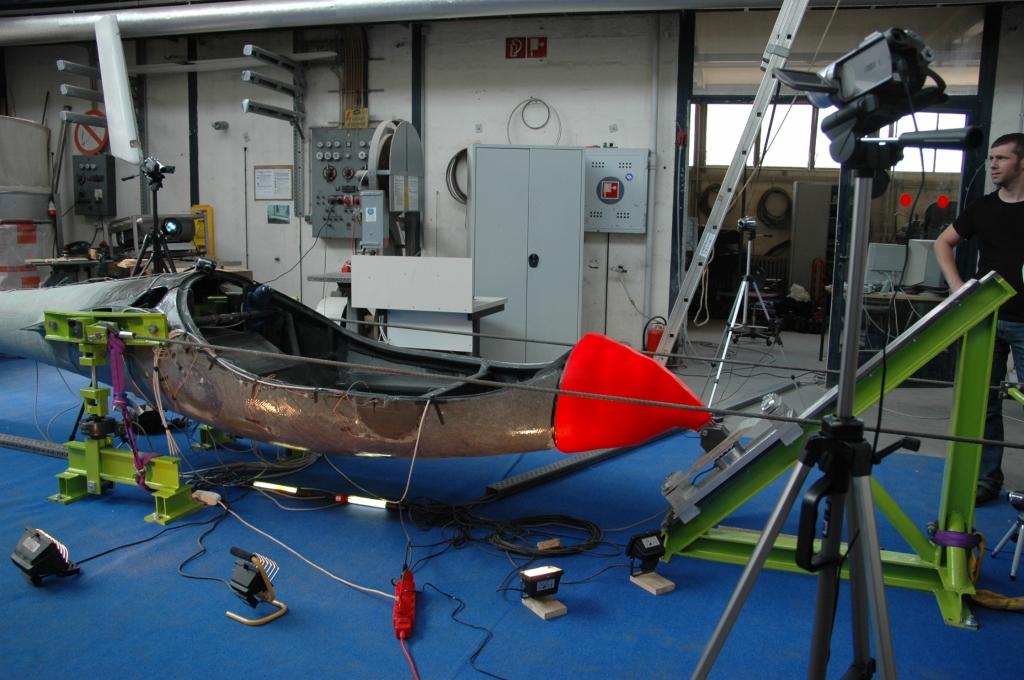
Fuselage

The ribs found in the tail section of the glider have been built and put in place to check sizing.

A mock-up version of the rear rib for shear forces has been built using glass fibre composites. It is glued to the boilerplate D-43 to assess whether the electric gear actuator can be attached to it.
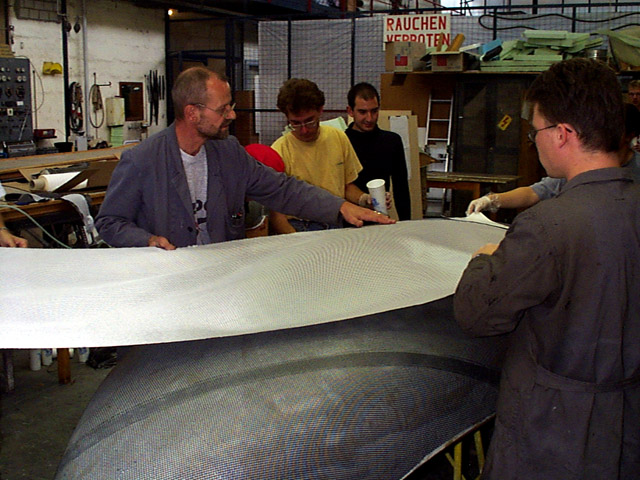
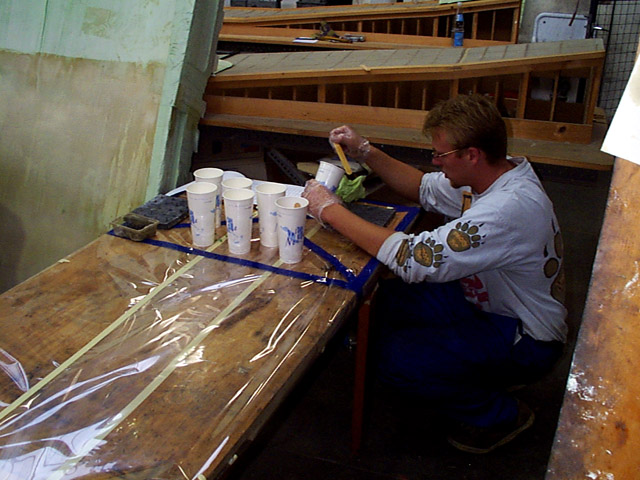
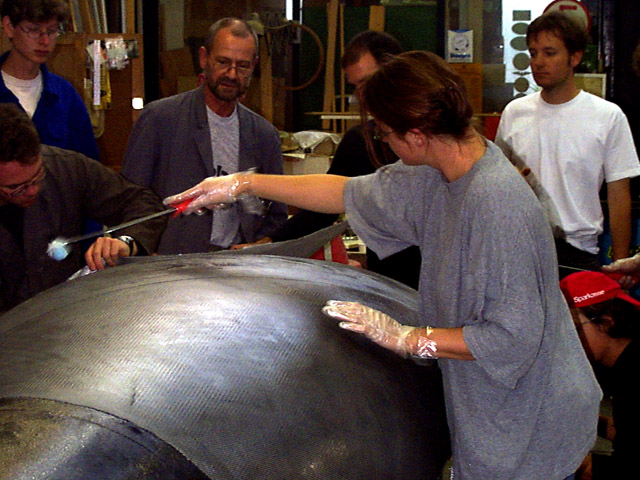



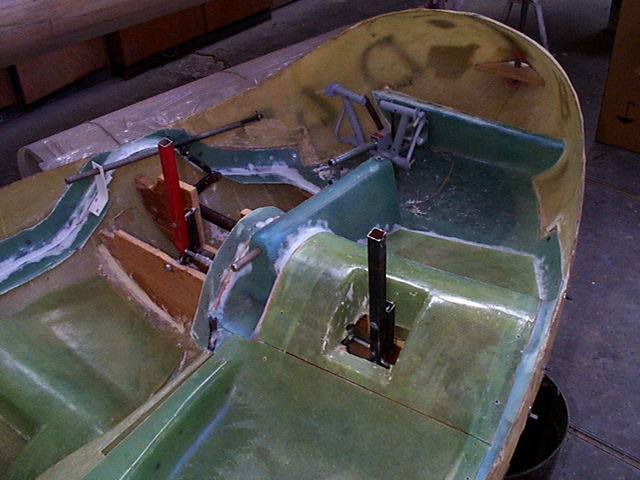
The seat pan is optimised using the mock-up.
Construction of the wing moulds
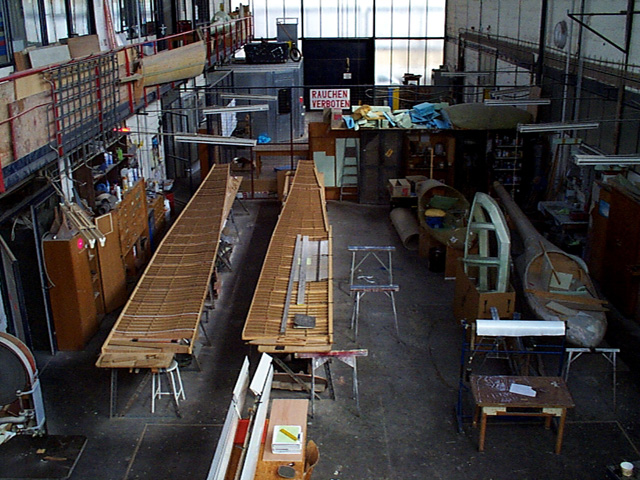
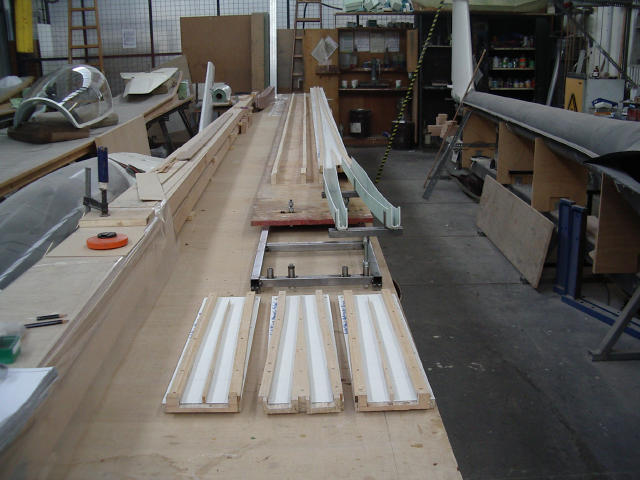


Carbon fibre belts for spar reinforcement were made from rovings using these moulds.
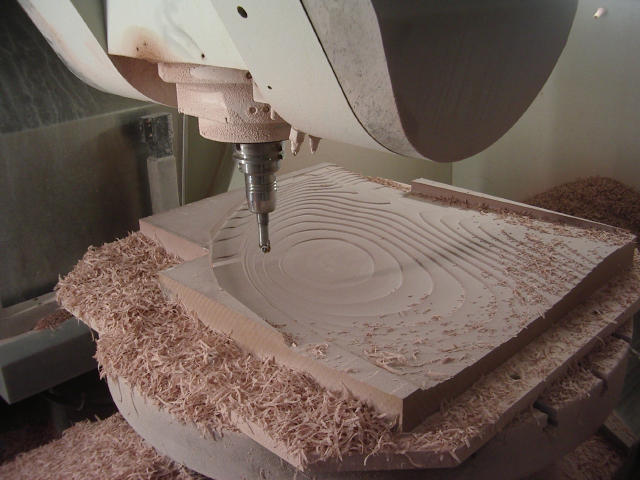

One half of a mould is being cnc-milled. It will later be used for the outermost part of the wing.
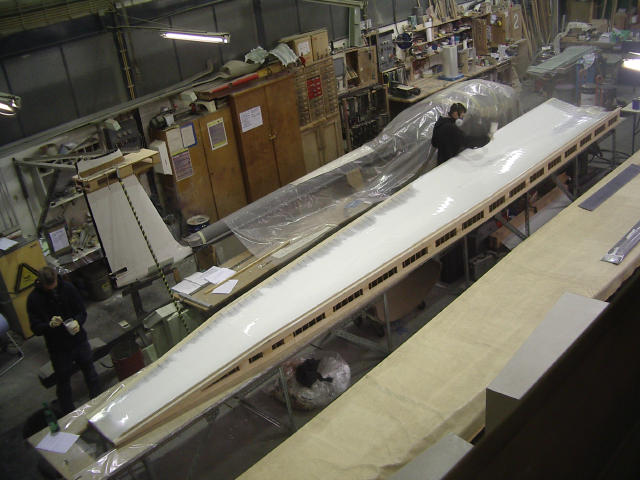

A wing mold is being painted. Once the wing is finished, it will already be covered in one layer of paint.
D-43’s wing
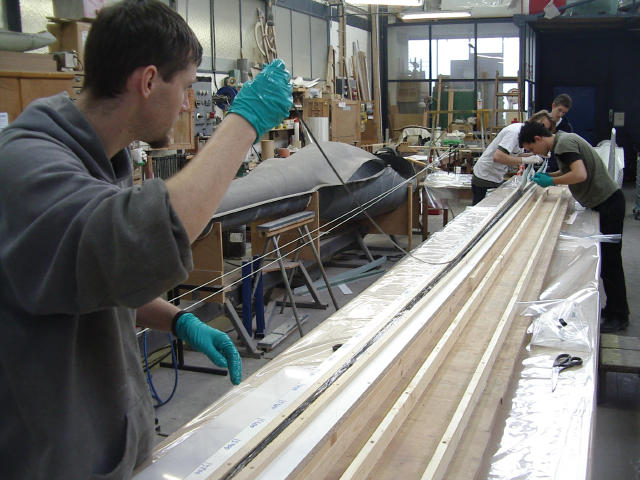

Carbon fibre rovings for the spar belts are pulled from a reel and soaked in resin.
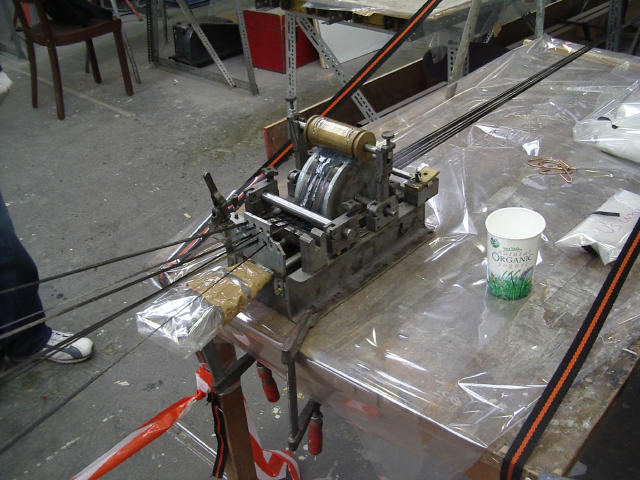
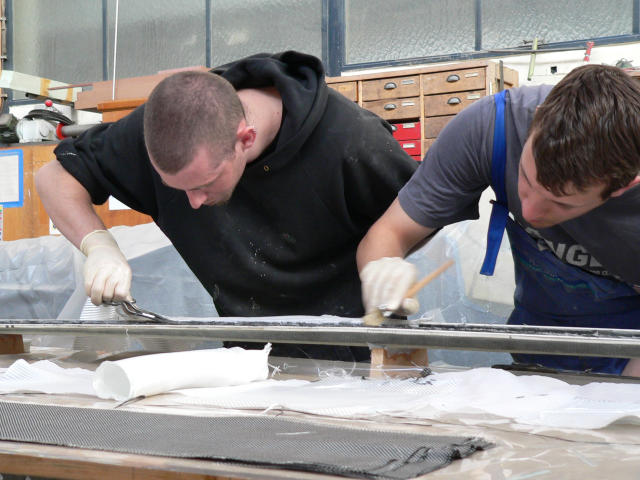



The attachment for the outermost part of the wing is being carefully aligned.

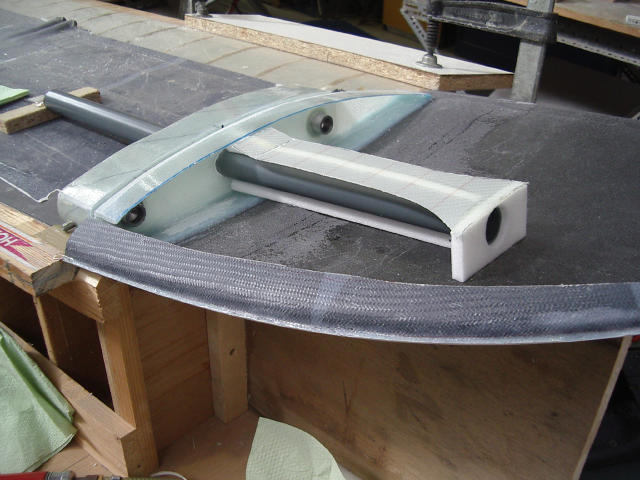
The control rods inside the wing will run through these bearings.
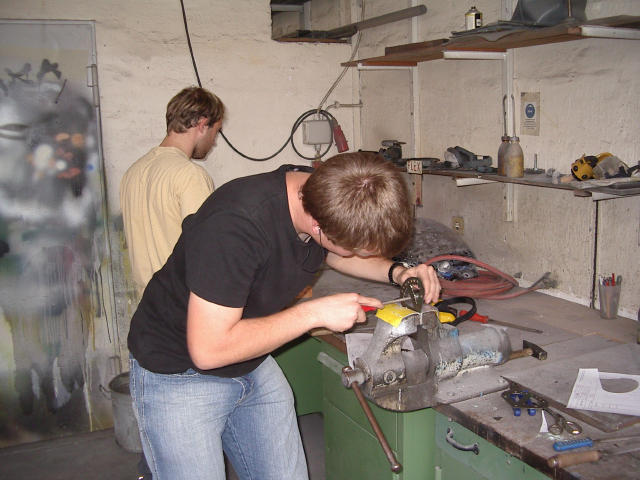

An aileron bell crank is being built.
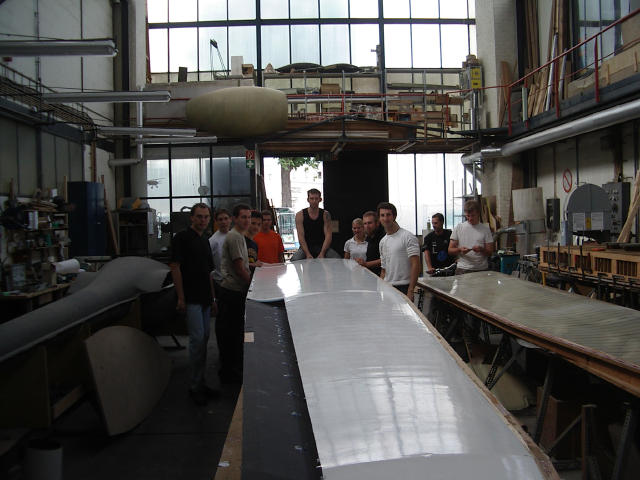

A fully bonded wing.
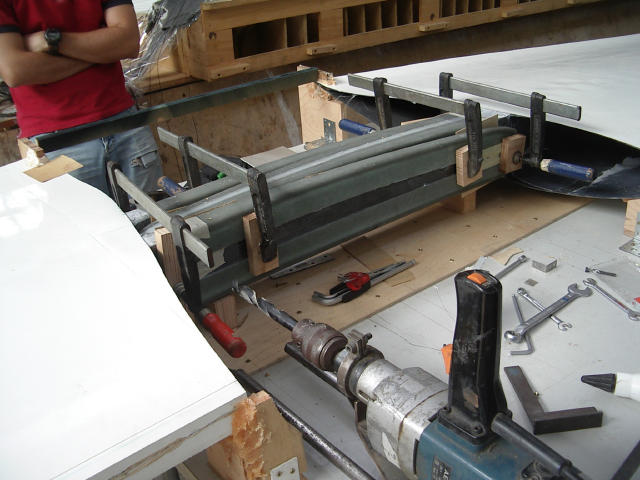

Holes are drilled into the connector part of the spar.
Fuselage
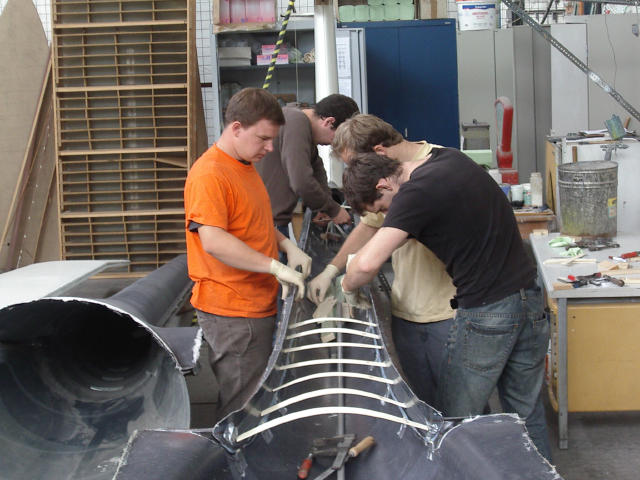

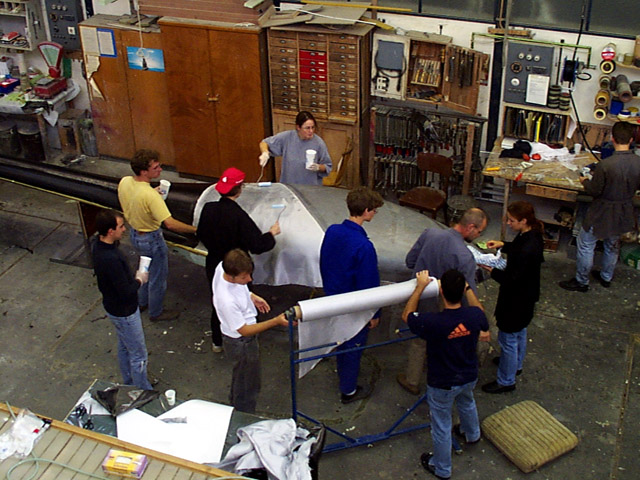
A “gluing flag” is attached in preparation for bonding the fuselage halves.
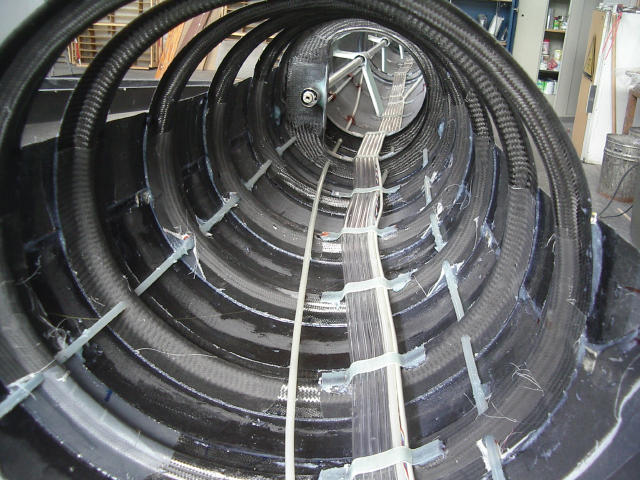

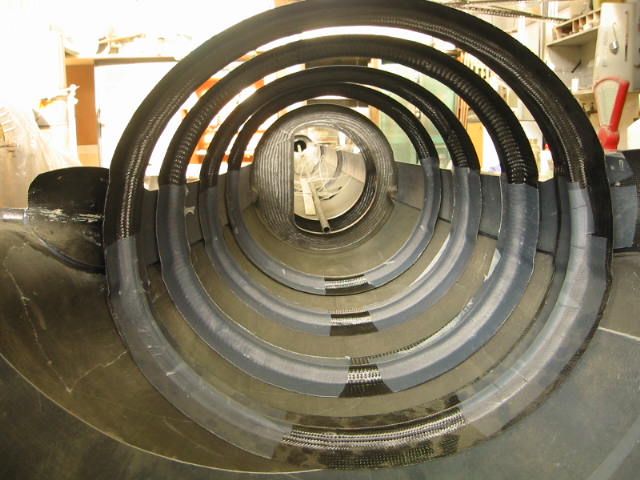
Circular ribs within the fuselage.
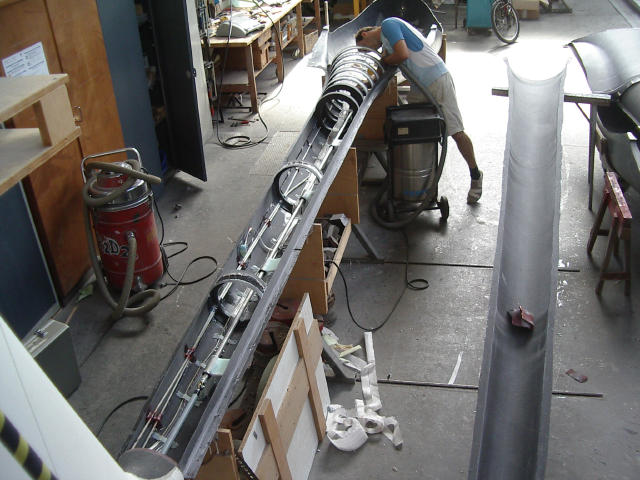

Circular ribs, static pressure probes and the elevator control rod are installed.
The wings are being stress-tested
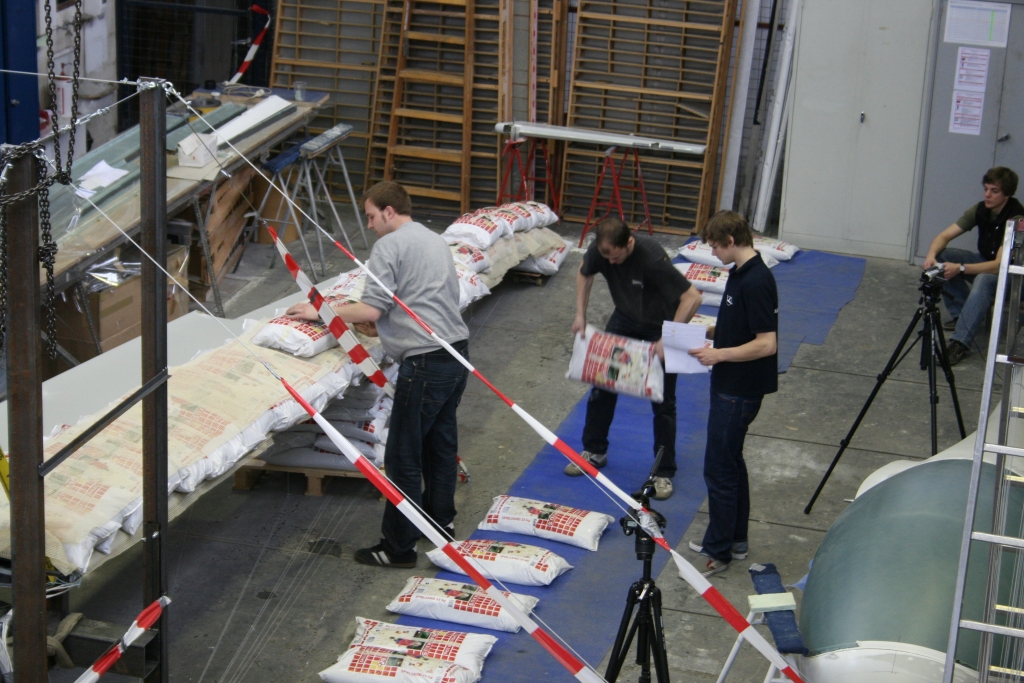
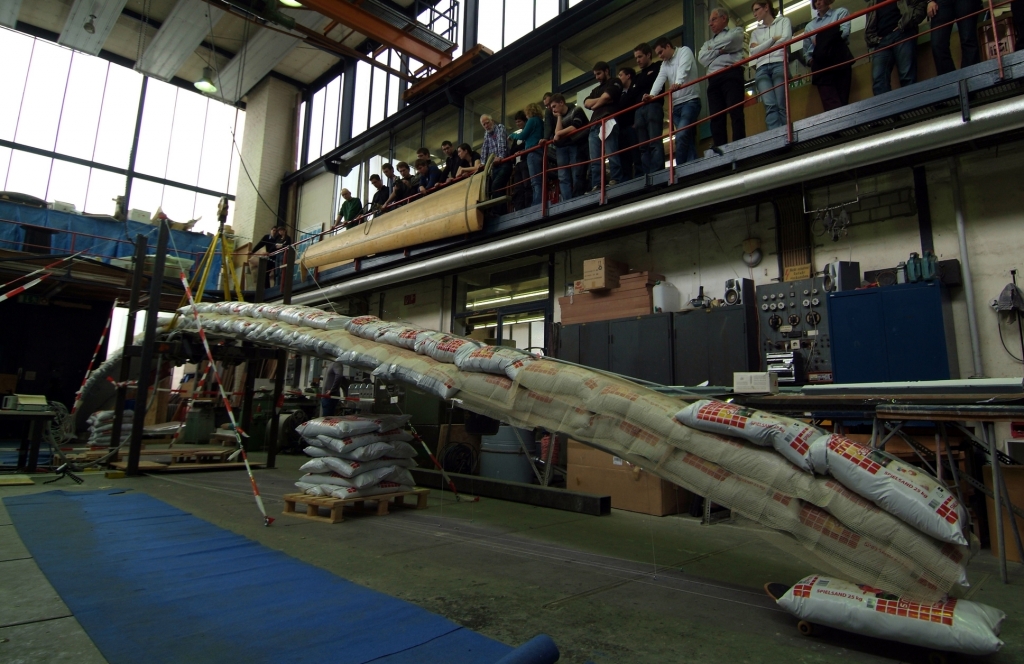


Destructive test of the fuselage


